Philippine Regions
Philippine regions identify the various areas throughout the country
The Philippines comprises more than 7,100 islands, but the 11 largest islands form most of the country’s land area.
The mountainous terrain includes many active volcanoes. The location of the Philippines just north of the equator gives the country a moderate tropical climate suited for the cultivation of export crops such as coconuts and pineapples. Agriculture has long formed the backbone of the economy.
Luzon, Visayas and Mindanao are the major Philippine Regions in the country. These areas are divided into 17 regions which are based on the geographical, cultural and ethnological characteristics of the country. Every region is divided into provinces which individually govern the local government units (districts, cities and towns) except the NCR. The National Capital Region (NCR) which is mainly the Metropolitan Manila or Metro Manila is the smallest administrative region in the country and the only region without any provinces. It is instead, subdivided into 17 local government areas (cities and municipalities), which are grouped together into districts for administrative purposes.
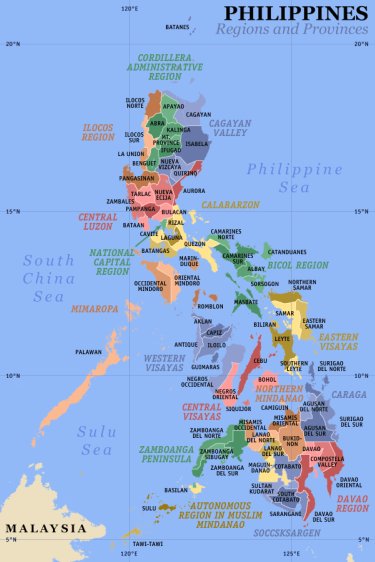
Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)
The Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) is the only one of the Philippine regions that is land-locked. It consists of the provinces of Abra, Apayao, Benguet, Ifugao, Kalinga, Mountain Province and Baguio City (the regional center). The Cordillera region encompasses most of the areas within the Cordillera Central mountain range of Luzon, the largest range in the country. This region is home to numerous indigenous tribes collectively called the Igorot.
Ilocos Region (Region I) - Philippine Regions
The Ilocos Region of the Philippines is located in the northwestern region portion of Luzon. It is bounded by the Cordillera Administrative Region and Cagayan Valley to the east, Central Luzon to the south and by the South China Sea to the west. The province of Pangasinan composes 58% of the region's population, 42% of its area and 61% of its economy.
The region is composed of four provinces, namely: Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, La Union and Pangasinan. Its regional center is San Fernando City, La Union. The Ilocano speaking people compose 66% of the region, the Pangasinan speaking people compose 27%, and the Tagalogs compose 3%.
Cagayan Valley (Region II) - Philippine Regions
Cagayan Valley is a region of the Philippines, also designated as Region II. It is composed of five provinces, namely: Batanes, Cagayan, Isabela, Nueva Vizcaya, and Quirino. It has three cities; Cauayan City, its regional center-Tuguegarao, and its commercial center-Santiago City.
Most of the region lies in a large valley in northeastern Luzon, between the Cordilleras and the Sierra Madre mountain ranges. The Cagayan River, the country's longest river runs through its center and flows out to Luzon Strait in the north, in the town of Aparri, Cagayan. The Babuyan and Batanes island groups that lie in the Luzon Strait also belong to the region.
Central Luzon (Region III) - Philippine Regions
Central Luzon, also known as Region III, is an administrative division or region of the Republic of the Philippines, primarily serve to organize the 7 provinces of the vast central plain of the island of Luzon (the largest island), for administrative convenience. The region contains the largest plain in the country and produces most of the country's rice supply, earning itself the nickname "Rice Bowl of the Philippines". Its provinces are: Aurora, Bataan, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Pampanga, Tarlac, and Zambales.
National Capital Region (NCR) - Philippine Regions
Metropolitan Manila or the National Capital Region (NCR) is the metropolitan region encompassing the City of Manila and its surrounding areas in the Philippines. It is composed of 16 cities—namely Manila itself, Caloocan, Las Piñas, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Navotas, Pasay, Pasig, Parañaque, Quezon City, San Juan, Taguig, Valenzuela—and the municipality of Pateros.
Metro Manila is the most populous of the twelve defined metropolitan areas in the Philippines. As of the 2007 census, it had a population of 11,553,427, comprising 13% of the national population. Including suburbs in the adjacent provinces (Bulacan, Cavite, Laguna, and Rizal) of Greater Manila, the population is around 20 million.
Calabarzon (Region IV-A) - Philippine Regions
Calabarzon is one of the regions of the Philippines. It is also designated as Region IV-A and its regional capital is Calamba City in Laguna. The region is composed of five provinces, namely: CAvite, LAguna, BAtangas, Rizal, and QueZON. The region's name is a portmanteau of the names of these provinces. The region is located in southwestern Luzon, just south and east of Metro Manila and is the second most densely populated region.
MIMAROPA (Region IV-B) - Philippine Regions
MIMAROPA is one of two regions of the Philippines having no land border with another region, Eastern Visayas being the other, and is designated as Region IV-B. The name is a portmanteau combining the names of its provinces, which are: Occidental Mindoro, Oriental Mindoro, Marinduque, Romblon and Palawan. There are many scenic spots in the MIMAROPA. Some of them are the Bathala Cave, Balanacan Bay and Tres Reyes Islands in the province of Marinduque; the White Island in Mindoro; Bonbon Beach in Romblon; and, the Puerto Princesa Subterranean River National Park and El Nido Marine Reserve Park in Palawan.
Bicol Region (Region V) - Philippine Regions
The Bicol Region occupies the Bicol Peninsula at the southeastern end of Luzon island and some other islands. It consists of six provinces, namely, Albay, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Catanduanes, Masbate, and Sorsogon. It has one independent component city, Naga City, and six component cities, Iriga, Legazpi, Ligao, Masbate, Sorsogon, and Tabaco. The regional centers are Legazpi City, the region's political and administrative center, Naga City, the region's cultural and religious center. Legazpi City, Naga City, and Sorsogon City are the leading cities in the region in terms of urbanization and also the hub of the region's economic activity.
Western Visayas (Region VI) - Philippine Regions
Western Visayas is designated as Region VI. It consists of six provinces; Aklan, Antique, Negros Occidental, Capiz, Guimaras and Iloilo and 17 cities making it the region with the highest number of cities. Iloilo City is the regional center.[1] The presence of almost all the government agencies' regional offices in the city and its geographical proximity to the other Region VI provinces affirm Iloilo City as the regional center.
Central Visayas (Region VII) - Philippine Regions
Central Visayas is located in the central part of the Visayas island group. It consists of four provinces—Bohol, Cebu, Negros Oriental, and Siquijor— and the highly urbanized cities of Cebu City, Lapu-Lapu City, and Mandaue City. The region is dominated by the native speakers of Cebuano. Cebu City is its regional center.
The land area of the region is 15,875 km². As of the 2007 census, it has a population of 6,398,628, making it the 5th most populous of the country's 17 regions.
Eastern Visayas (Region VIII) - Philippine Regions
Eastern Visayas is one of the two regions of the Philippines having no land border with another region, MIMAROPA being the other, and is designated as Region VIII. It consists of six provinces, namely, Biliran, Eastern Samar, Leyte, Northern Samar, Samar and Southern Leyte. These provinces occupy the easternmost islands of Visayas: Leyte, Samar and Biliran. The regional center is Tacloban City.
Eastern Visayas is primarily an agricultural region with rice, corn, coconut, sugarcane and banana as major crops. Its total land area is 21,431.7 km². 52% of its total land area are classified as forestland and 48% as alienable and disposable land.
Zamboanga Peninsula (Region IX) - Philippine Regions
Zamboanga Peninsula is a peninsula and an administrative region in the Philippines. Designated as Region IX, the region consists of three provinces, namely, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, and Zamboanga Sibugay, its component cities of Dipolog, Dapitan, Pagadian, and Isabela (Capital of Basilan Province, which is a part of the ARMM) and the chartered city of Zamboanga. Pagadian City is the regional center.
The region has vast forest resources and previously used to export logs, lumber, veneer and plywood. Mineral deposits include gold, chromite, coal, iron, lead, and manganese. Among its non-metallic reserves are coal, silica, salt, marble, silica sand, and gravel. Its fishing grounds are devoted to commercial and municipal fishing. It has also aqua farms for brackish water and freshwater fish.
Northern Mindanao (Region X) - Philippine Regions
Designated as Region X of the Philippines, Northern Mindanao is composed of five provinces and two cities classified as highly-urbanized, all occupying the north-central part of Mindanao island, and the island-province of Camiguin. The regional center is Cagayan de Oro City, where the national government's regional offices and other big establishments are located More than 60% of Northern Mindanao's total land area are classified as forest land. Its seas abound with fish and other marine products.
Davao Region (Region XI) - Philippine Regions
Davao Region, designated as Region XI, is one of the regions of the Philippines, located on the southeastern portion of Mindanao. Davao Region consists of four provinces, namely: Compostela Valley, Davao del Norte, Davao Oriental, and Davao del Sur. The region encloses the Davao Gulf and its regional center is Davao City. Aside from its forestland and fertile fields, Southern Mindanao has mineral resources of chrornite, iron, nickel, and manganese, gold, copper and other non-metallic minerals. Five of the major fishing grounds of the Philippines are located in the region.
SOCCSKSARDEN (Region XII) - Philippine Regions
SOCCSKSARGEN is located in central Mindanao, and is officially designated as Region XII. The name is an acronym that stands for the region's four provinces and one of its cities: South Cotabato, Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, Sarangani and General Santos City. The regional center is Koronadal City located in the province of South Cotabato. Cotabato City, though geographically within the boundaries of the province of Maguindanao, itself is part of SOCCSKSARGEN, and is independent of that province. Maguindanao province is a part of another special region called the ARMM which has its seat in Cotabato City. SOCCSKSARGEN and the province of Maguindanao were once part of the original Cotabato province.
Caraga (Region XIII) - Philippine Regions
Caraga is an administrative region of the Philippines, on the northeastern portion of the island of Mindanao. It is the newest region in the Philippines, and is also called Region XIII. The Caraga Region was created through Republic Act No. 7901 on February 25, 1995. The region is composed of five (5) provinces: Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Dinagat Islands, Surigao del Norte and Surigao del Sur; five (5) cities: Butuan, Surigao, Bislig, Cabadbaran and Tandag; seventy (70) municipalities and 1,346 barangays. Butuan City is the regional center.
Rich in natural resources, the region has large tracts of land available for development. The region is noted for its wood based economy, its extensive water resources and its rich mineral deposits such as iron, gold, silver, nickel, chromite, manganese and copper. Its leading crops are palay, banana and coconut. It has excellent tourism potentials because of its unspoiled and beautiful beaches, abundant and fresh seafood, ancient and historical landmarks, hot and cold springs, evergreen forests and balmy weather.
Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) - Philippine Regions
The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao is in Mindanao Island of the Philippines, that is composed of all the Philippines' predominantly Muslim provinces, namely: Basilan, Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, Sulu and Tawi-Tawi, and the Islamic City of Marawi. It is the only region that has its own government. The regional capital is at Cotabato City, although this city is outside of its jurisdiction. The ARMM previously included the province of Shariff Kabunsuan until July 16, 2008, when Shariff Kabunsuan ceased to exist as a province after the Supreme Court in Sema v. Comelec declared unconstitutional the "Muslim Mindanao Autonomy Act 201", which created it.
The region is divided into two geographical areas – the Mindanao mainland and the Sulu Archipelago. Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao and Shariff Kabunsuan are situated in the Mindanao mainland, while Basilan, Sulu and Tawi-Tawi are located within the Sulu Archipelago. ARMM covers a total of 12,288 km².
Tagalog: mga rehiyon ng Pilipinas (region of the Philippines)


