Physical Map of the Philippines
On a physical map of the Philippines, you will see that the Philippines is located just south-east of Asia. It is an off-shore archipelago bounded by water on all sides.
The Pacific Ocean forms the eastern border, the Celebes Sea to the south, the South China Sea borders the west and north. Depending on high tide or low tide, there about 7,107 islands in the Philippines, of which approximately 1,000 are inhabited.
The Philippines topography is separated by numerous seas resulting in one of the most extensive coastlines of any country. A large percentage of Filipinos reside somewhere near the ocean, where small-scale fishing is quite normal to earn a living.
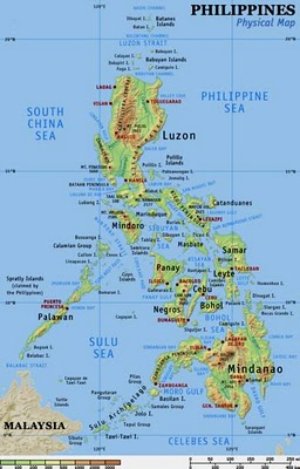
Physical Map of the Philippines (Click to Enlarge)
The primary groupings of the islands consist of 3 areas: Luzon in the north, is the largest covering about 141,395 square kilometers; Visayas is in the center covering about 56,606 square kilometers; and Mindanao is in the south covering about 102,000 square kilometers. As seen on a physical map of the Philippines some of the other prominent islands are Samar, Negros, Palawan, Panay, Mindoro, Leyte, Cebu, Bohol and Masbate.
The Philippines is situated within the Pacific 'Ring of Fire', where there are numerous active volcanoes. In addition, all of the Philippine islands are susceptible to earthquakes.
Luzon - Northern Philippines
The island of Luzon contains several well-known mountains and mountain ranges. One of the most famous is Mount Mayon, not far from Legazpi City. Last erupting in 2006, it is a fairly active volcano. Mt. Mayon rests in the middle of Mayon Volcano National Park and is really popular with climbers, hikers, and campers.
Mount Pinatubo, also on Luzon Island, had a huge eruption in June 1991, resulting in extensive damage to the surrounding areas. This also led to the eventual closure of the United States' Clark Airbase, and the following year closure of Subic Bay naval base.
Located approximately 50 kilometers to the south of Manila is Taal Lake and Taal Volcano. Massive eruptions thousands of years ago created a caldera or crater which formed into a lake, with further eruptions creating islands within the lake. Today, it is definitely one of the most picturesque scenes in the country.
Mountain ranges on Luzon include the northern Luzon highlands, or Cordillera Central, rising to between 2,500 and 2,750 meters, and the Sierra Madre Mountain Range in the northeastern portion of Luzon.
Rivers in Luzon consist of the Cagayan in northern Luzon, and the Pampanga, which flows south from Central Luzon into Manila Bay.
Laguna de Bay has the distinction of being the Philippines largest freshwater lake and lies just east of Manila as shown on a physical map of the Philippines.
Visayas - Central Philippines
Mt. Canlaon on Negros Island, central Philippines, is also an active volcano. It's located right at the border of Negros Oriental and Negros Occidental provinces. Of interest to visitors are the 3 hot springs on the slopes of the mountain: Mambucal Hot Springs, Bucalan Hot Spring, and Bungol Hot Spring.
Mindanao - Southern Philippines
Mindanao is mountainous and contains the Philippines highest peak, Mount Apo. Specifically located between Davao City and Davao del Sur as indicated on a physical map of the Philippines , it is referred to as Apo, which means ancestor. Even though it is possibly an active volcano, no eruptions have been recorded. Mt. Apo is by far the most popular destination for climbers in the country.
The major rivers in Mindanao are the Pulangi River, which flows into the longest river in Mindanao, the Mindanao River or Rio Grande de Mindanao, and the Agusan, which flows north into Butuan Bay.


